The cannabis plant contains up to 545 chemical compounds, including over 100 different cannabinoids which may interact with the body’s cannabinoid receptors. This plant has been studied and used for many years for its potentially therapeutic benefits. In Australia, cannabis became legal for medical use in 2016, permitting access through a doctor’s prescription. The cannabis plant comprises numerous components, including various strains serving different purposes. The most common cultivars in Australia are Indica and Sativa, each with their own unique properties and characteristics.
What is a cannabis plant?
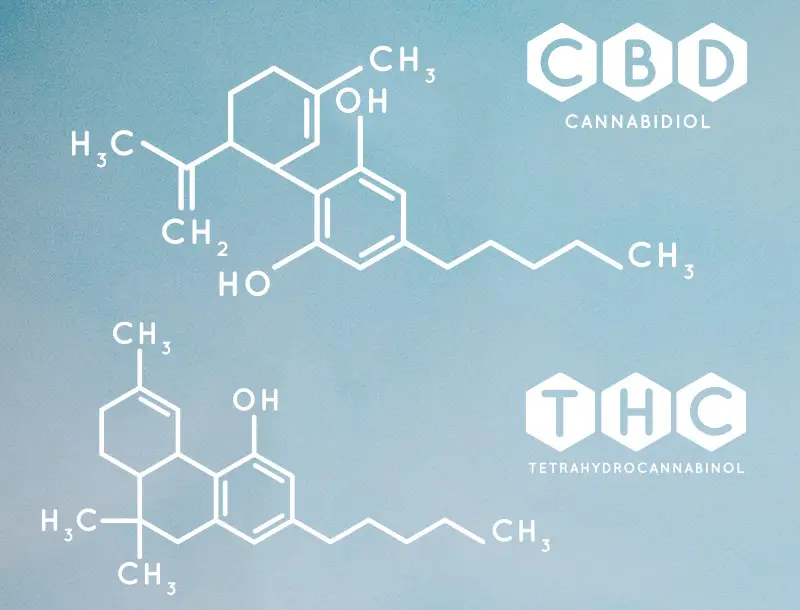
The cannabis plant, from the Cannabaceae family, is a botanical specimen with a rich history. Recognised for its potential therapeutic properties, the plant contains over 100 unique compounds known as cannabinoids. Notably, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are two prominent cannabinoids that have garnered significant attention for their possible medical applications. THC is known for its psychoactive effects, while CBD is non-intoxicating. Both are being studied to explore potential uses within a medicinal context. It should be noted that referring to cannabis as though it were one type of medicine is misleading. There are various forms that medicinal cannabis can take as well as a range of strengths and varieties.
What is the medical history of the cannabis plant?
The cannabis plant has been used medicinally since 1000 BC, initially as an anaesthetic. It was introduced from India to Europe around the mid-19th century and used for a variety of conditions by the early 20th century. However, chemists were unable to create a consistent product because the active ingredients were unknown. By the mid-20th century, cannabis became illegal in most countries around the world and its usage by the medical community ceased.
In 1965, Raphael Mechoulam and Yehiel Gaoni isolated THC for the first time, which led to a flurry of investigations. Twenty five years later, Mechoulam discovered endogenous cannabinoids as well as the endocannabinoid system, which again reignited interest and research into the plant. The last twenty years has seen a gradual, world-wide re-adoption of cannabis for medical purposes. It has been legalised in Australia, Canada, Israel, the United Kingdom, NZ, many US States, as well as several European countries including but not limited to Germany, Italy, the Netherlands and Finland.
In the last 45 years, there have been over 1,000 studies conducted using medicinal cannabis, with most of those studies being published in the last decade. This renewed global interest in medicinal cannabis has led to a better understanding of the cannabis plant and identification of many more active components. Ongoing research continues to unveil the potential benefits and risks associated with the cannabis plant, fostering a deeper understanding of its intricate pharmacology and therapeutic possibilities.
Help is at Hand
Get free information and assistance quickly by filling out the contact form below.

What are the different parts of the cannabis plant?
The cannabis plant consists of several distinct parts. Each part contributes to its overall structure and function of the plant. At the core is the flowering structure, the bud, which contains the highest concentration of cannabinoids. Within the bud, resin-producing glands called trichomes house the cannabinoids, terpenes, and other phytocompounds. Leaves, the most recogniseable feature, come in various shapes and sizes and play a crucial role in photosynthesis. Stems provide structural support and serve as conduits for nutrient transport. Roots anchor the plant in soil and absorb water and nutrients.
Male vs female cannabis plants
One pivotal aspect of cannabis cultivation is understanding the difference between male and female plants. Female plants produce the coveted flowers rich in cannabinoids, while males generate pollen for fertilisation. Cultivators typically seek female plants for their cannabinoid content, while removing males to prevent seed development, which can diminish flower quality. This selection process is integral to controlled cultivation and the production of high-quality cannabis for medical use. The ability to distinguish and manage male and female plants is a fundamental skill for manufacturers seeking optimal yield and potency in their cannabis crops.

What are the different types of cannabis plants?
Cannabis plants are commonly categorised into three main types: indica, sativa, and a combined hybrid of these. Each type possesses unique characteristics, including morphology, growth patterns, and environmental adaptations. Indica is known for its short appearance and fares best in colder climates, whereas sativa hails from warmer regions and appears tall and slender. Hybrids can take on a range of these characteristics depending on their specific makeup.
Indica
Indica plants are characterised by their relatively short stature and compact, bushy structure. The leaves of indica plants are broad, and the plant typically has a darker green colour. Originating from mountainous regions with challenging climates, such as the Hindu Kush mountain range in Afghanistan, indica plants have developed adaptations to withstand colder temperatures and shorter growing seasons. These robust plants are well suited for indoor cultivation due to their manageable size and efficient use of space. Indica strains are often associated with potential relaxing effects, but it’s important to note that the effects can vary widely based on the plant’s chemical composition.
Sativa
Sativa plants display a more elongated and slender structure than indica plants. They feature a thinner and lighter-coloured leaf. Hailing from regions near the equator with long growing seasons, such as parts of Africa, Central America, and Southeast Asia, sativa plants have adapted to thrive in warmer climates. Their height and open structure make them suitable for outdoor cultivation, where they can reach impressive heights. Sativa strains, compared to indica strains, are believed to have more uplifting or energising effects, though individual variations can be considerable.
Contact Us For Free Assistance
"*" indicates required fields
Additional Information on Cannabis Strains
Learn more about the legal landscape surrounding medical cannabis strains in Australia, including regulations governing cultivation, prescription, and usage for therapeutic purposes.
The Legality of Cannabis StrainsLearn about the diverse effects of medical cannabis strains, from energizing sativas to relaxing indicas, and how they can be tailored for Australian patients’ unique therapeutic needs.
Effects of Cannabis StrainsMedical cannabis strains are varieties of the cannabis plant with distinct characteristics, chemical compositions, and potential therapeutic effects, allowing healthcare professionals to tailor treatments to individual patient needs.
Medical Cannabis Strains AustraliaLearn about the diverse world of cannabis strains and their applications in various medical cannabis products, from oils and edibles to vaporised flowers and topicals tailored for Australian patients.
Cannabis Strains and Product TypesLearn about how the cannabis plant is made up of many chemical compounds that contribute to the look, flavour, scent, and effect of the plant.
Chemical Makeup of Cannabis