The endocannabinoid system is an important system to be aware of when considering medicinal cannabis as a treatment option. Medicinal cannabis products primarily interact with the endocannabinoid system to bring about therapeutic medical effects. The endocannabinoid system provides an important balance for a lot of biological functions. The exact effects are determined largely by the phytocompounds (chemical compounds derived from plants) ingested and how they interact with the cannabinoid receptors in the human body. Sometimes they can act in tandem to enhance the overall effects in a phenomenon known as the entourage effect. Taking care of the endocannabinoid system is important, as endocannabinoid deficiencies have been linked to a range of negative health outcomes.
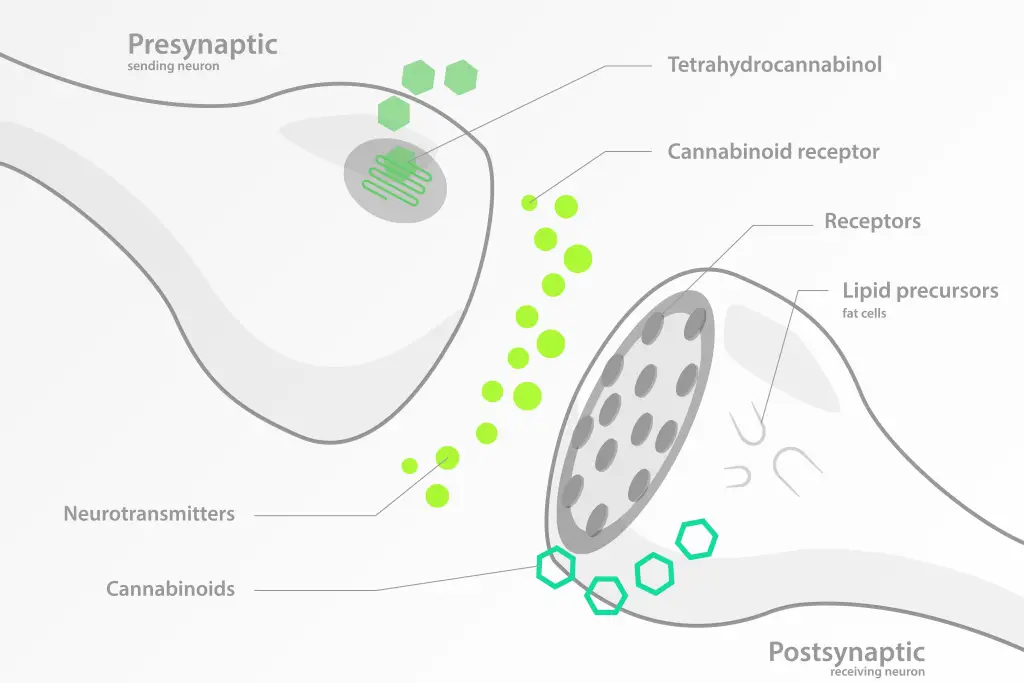
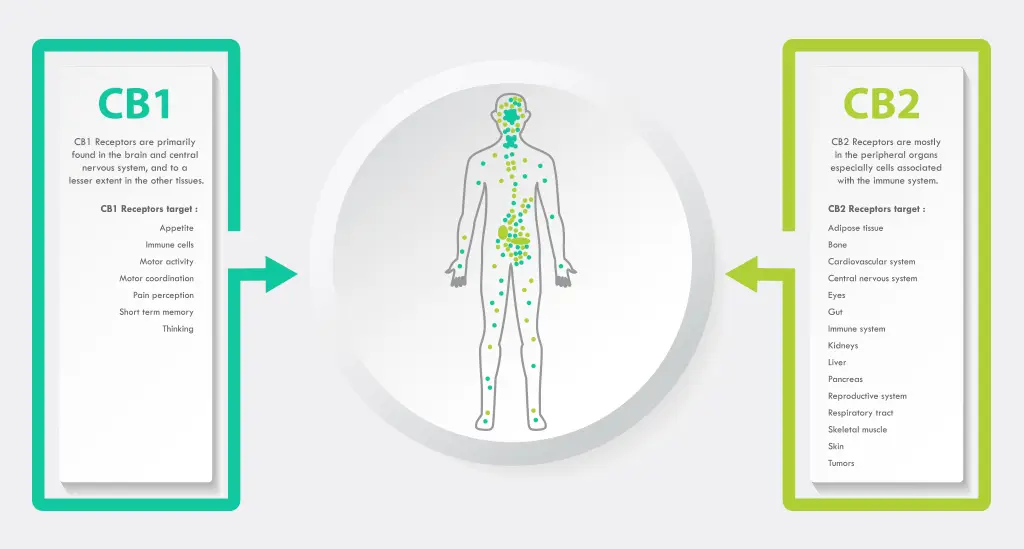
What is the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system is a network within the human body made up of cannabinoid receptors. These receptors are essentially cell proteins that respond to chemicals, specifically cannabinoids. They react to both cannabinoids that come from within the human body (endocannabinoids) and cannabinoids from external sources that are consumed. While the research surrounding the endocannabinoid system is still in preliminary stages, it is linked to a variety of body processes. The endocannabinoid system is thought to have a role in regulating physiological processes, the immune system, appetite, pain, emotions and more.
How does the endocannabinoid system work?
The endocannabinoid system works by responding to stimulation of its receptors. Depending on how cannabinoids interact with these receptors, different effects can occur within the human body. The exact effects depend on the compounds at play. Our bodies produce their own selection of cannabinoid compounds naturally that stimulate our receptors. But this effect can often be replicated by ingesting cannabinoids that derive from the cannabis plant, such as from medical cannabis.
Endocannabinoid receptors
The two primary types of endocannabinoid receptors are called the CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are located mainly in the brain and central nervous system. However, some also exist among peripheral organs and tissues. Due to their connection with the brain and central nervous system, strong interactions with these receptors have the potential to create psychoactive effects. CB2 receptors are dispersed among the peripheral immune system and in specific areas of the central nervous system.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are compounds naturally produced by the human body. They are lipid-signalling molecules that stimulate the receptors when the system recognises a necessity for it. The two primary types of endocannabinoids are anandamide (AEA or arachidonoyl ethanolamide) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). AEA can be found in nearly all types of tissue, and primarily binds to the CB1 receptors, in a similar way to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). 2-AG is primarily found within the brain, and binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Phytocannabinoids
Phytocannabinoids are molecules that come from the cannabis plant. When consumed, they are able to interact with the endocannabinoid system in a similar way to endocannabinoids. Each cannabinoid has a different way of affecting the cannabinoid receptors. For example when THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system, it binds to the CB1 receptors. Since they are located in the brain and central nervous system, this can result in certain psychoactive effects. This is in contrast to cannabidiol (CBD). When CBD interacts with the cannabinoid receptors, it doesn’t bind in the way THC does. This results in slightly different effects. It’s part of the reason CBD-based products like CBD oil are popular as less intense alternatives to THC.
Other phytocompounds
While the endocannabinoid system primarily deals with cannabinoids, recent research suggests that other phytocompounds may also interact with the receptors. Terpenes and flavonoids in particular are thought to have benefits we were not previously aware of.
Entourage effect
The entourage effect is when different phytocompounds from the cannabis plant interact in tandem to enhance the overall effect. While it was originally believed that cannabinoids and other compounds worked separately, recent research suggests that they may interact. One example is CBD potentially dampening the psychoactive effects of THC. Certain terpenes and flavonoids have also been highlighted as potentially benefiting the efficacy of medical cannabis when paired with the appropriate cannabinoids.
What is the purpose of the endocannabinoid system?
The primary purpose of the endocannabinoid system seems to be keeping the body’s functions in homeostasis. While more research is required, it has been linked to both physiological and cognitive processes in the human body. A well-functioning endocannabinoid system is thought to provide benefits for sleep, immune health, appetite management and mood amongst other things.
Endocannabinoid deficiency
Endocannabinoid deficiency refers to when someone’s body is producing a shortage of endocannabinoids. This can result in a range of different health conditions. Conditions such as migraines, fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome have all been linked to endocannabinoid deficiency. Endocannabinoid deficiency can be addressed with solutions such as exercise, increased omega-3 intake, stress management and intake of phytocannabinoids.


Have questions?
Our friendly team is available to assist you with any queries.
Want to learn more?
Little Green Pharma is dedicated to providing useful educational materials for anyone interested in learning. Head to our medical cannabis hub to find more informative articles related to medical cannabis. If you’re interested in learning about our product selection, check our product hub or contact us today.